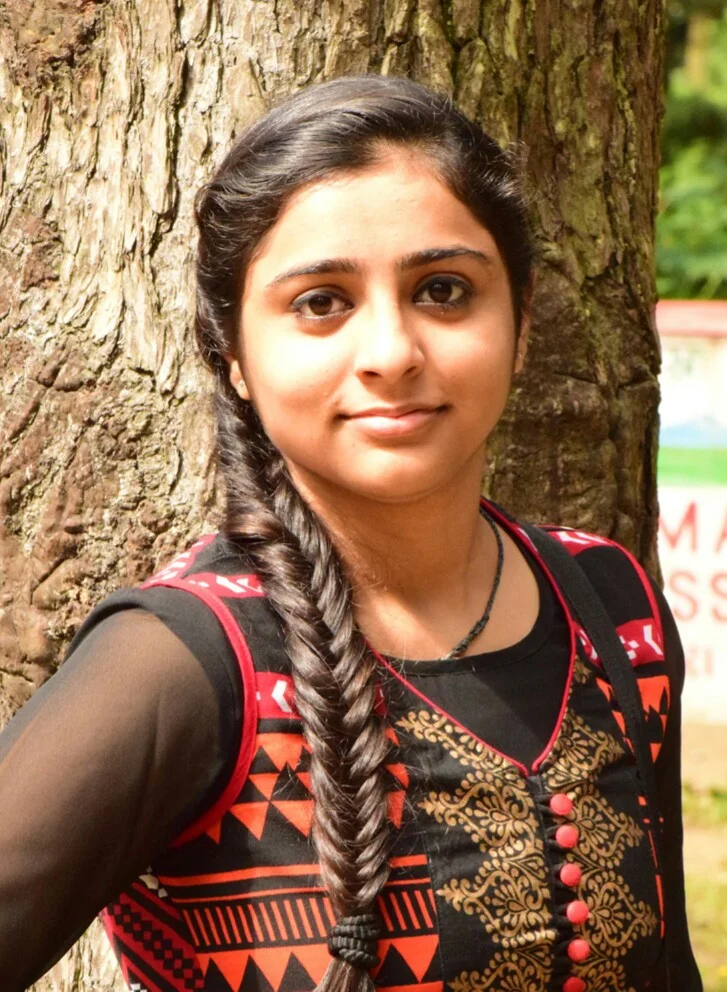
A humanoid robot system that can translate commands from natural language straight into robot behaviours has been developed by researchers at Alternative Machine and the University of Tokyo. The robot, called Alter3, is intended to leverage the extensive information found in large language models (LLMs) like GPT-4 to carry out intricate tasks like posing as a ghost or snapping a selfie.
This research is the most recent in an expanding series that combines robotics systems and foundation model power. Although scalable commercial solutions for these systems are still a ways off, they have spurred advancements in robotics research in recent years and hold great potential.
Also Read: Humanoid Robots and the Role of AI in Transforming Technology
Robot Controlled by LLMs
GPT-4 is the backend model used by Alter3. A natural language command that either explains an action or a circumstance that the robot needs to react to is given to the model.
The LLM plans a sequence of steps that the robot needs to execute to accomplish its objective using an “agentic framework.” The model serves as a planner in the first stage, figuring out the steps needed to carry out the intended action.
Also Read: IEEE Forms Group for Humanoid Robot Safety and Performance Standards
After that, a coding agent receives the action plan and uses it to create the commands needed for the robot to carry out each step. Because GPT-4 has yet to be taught on Alter3’s programming commands, the researchers utilize its capacity for in-context learning to modify its behaviour to match the robot’s API. This indicates that a list of commands and a series of examples demonstrating the use of each command are included in the prompt. Next, the model associates each step with one or more API commands that are transmitted to the robot for implementation.
The researchers state, “We had to control all 43 axes in a specific order before the LLM appeared to mimic a person’s pose or to pretend a behaviour such as serving tea or playing chess.” “We are no longer burdened with the repetitive tasks because of LLM.“
Gaining knowledge via user feedback
The most precise vehicle for describing physical positions is not language. As a result, the action sequence that the model generates may not precisely cause the robot to behave as intended.
The researchers have included functionality that enables others to offer comments, such as “Raise your arm a bit more,” to encourage repairs. Another GPT-4 agent receives these instructions, analyzes the code, makes the required adjustments, and sends the action sequence back to the robot. For later use, the code and improved action recipe are kept in a database.
Also Read: Is China’s Humanoid Robot Industry a marketing ploy or a sign of the Robotic Revolution?
Alter3 was put to the test by the researchers using a variety of tasks, including mimicking gestures like posing as a snake or a ghost and commonplace actions like drinking tea and snapping selfies. The model’s capacity to react to situations requiring meticulous action planning was also put to the test.
A wide variety of language representations of movements are included in the LLM’s instruction. According to the researchers, GPT-4 can map these representations precisely onto Alter3’s anatomy.
GPT-4’s vast understanding of human motions and behaviours allows for the development of more realistic behaviour plans for humanoid robots, such as Alter3. According to the researchers’ experiments, they were also able to replicate in the robot feelings like delight and humiliation.
The researchers believe that “the LLM can infer adequate emotions and reflect them in Alter3’s physical responses, even from texts where emotional expressions are not explicitly stated.”
More sophisticated models
In robotics research, the use of foundation models is growing in popularity. For instance, the $2.6 billion Figure leverages OpenAI models in the background to comprehend commands from humans and perform tasks in the actual world. Robotics systems will become more capable of reasoning about their surroundings and making decisions as multi-modality becomes the standard in foundation models.
Also Read: China Ex-Robots Develop Humanoids With Facial Movement & Emotional Intelligence
Alter3 is among a group of initiatives that leverage commercially available foundation models as modules for planning and reasoning in robotic control systems. The researchers note that Alter3 does not employ an optimized version of GPT-4 and that other humanoid robots can utilize the code.
Some projects, like OpenVLA and RT-2-X, use specific foundation models that are intended to generate robotic commands directly. These models typically yield more consistent outcomes and exhibit greater task and environmental generalization. However, they cost more to produce and call for specialized knowledge.
A common oversight in these initiatives is the fundamental difficulties involved in building robots capable of simple functions like gripping objects, keeping their equilibrium, and moving.
Also Read: AI Humanoid ‘Reachy2’ by Hugging Face and Pollen Robotics Debuts in New Video